Arizona suspends uber self driving tests – Arizona suspends Uber self-driving tests: The news dropped like a bomb in the autonomous vehicle world. Suddenly, Uber’s ambitious Arizona program, once a symbol of self-driving progress, was grounded. This wasn’t just a minor setback; it sent shockwaves through the industry, raising questions about safety regulations, technological readiness, and the very future of driverless cars. What exactly happened to trigger this sudden halt, and what does it mean for the future of self-driving technology?
The incident involved a self-driving Uber vehicle and its interaction with a pedestrian, leading to the immediate suspension of all autonomous vehicle testing in the state. This decision highlights the complex interplay between technological advancement and regulatory oversight in the rapidly evolving field of autonomous vehicles. The fallout extends beyond Uber itself, impacting investor confidence, public perception, and the broader trajectory of self-driving car development.
Background of Uber’s Self-Driving Program in Arizona
Uber’s foray into autonomous vehicle testing in Arizona was a significant chapter in the state’s burgeoning self-driving car scene, ultimately ending in a high-profile suspension. This involved a complex interplay of technological ambition, regulatory frameworks, and unforeseen incidents. Understanding the program’s history is crucial to analyzing the reasons behind its abrupt halt.
Uber’s self-driving technology in Arizona relied on a combination of sophisticated sensors, including lidar, radar, and cameras, to create a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s surroundings. This data was then processed by complex algorithms to navigate roads, identify obstacles, and make driving decisions. The system was designed to handle various traffic situations, but, as events would prove, not all.
Timeline of Uber’s Self-Driving Operations in Arizona
Uber began testing its self-driving vehicles in Arizona in 2016, initially operating in Tempe and later expanding to other areas. The initial phase focused on mapping routes and gathering data on road conditions and traffic patterns. As confidence in the system grew, Uber gradually increased the number of vehicles on the road and the complexity of the routes they traversed. This expansion was undertaken within the existing regulatory framework for autonomous vehicles, which at the time was relatively permissive compared to other states.
Regulatory Environment for Autonomous Vehicles in Arizona
Prior to the suspension of Uber’s testing, Arizona had established itself as a relatively welcoming environment for autonomous vehicle development. The state legislature passed legislation that aimed to balance innovation with safety concerns. This approach involved a permitting process for autonomous vehicle testing, but it did not impose overly stringent restrictions on the number of vehicles or the types of routes they could operate on. This relatively open regulatory environment was seen by many as a key factor in attracting companies like Uber to conduct testing in the state. The regulatory environment, however, proved not entirely equipped to handle the unforeseen consequences of a rapidly evolving technology.
Key Events Leading to the Suspension of Uber’s Self-Driving Tests
The following table summarizes key events that ultimately led to the suspension of Uber’s self-driving program in Arizona.
| Date | Event | Location | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | Uber begins self-driving car testing in Tempe, Arizona. | Tempe, Arizona | Establishment of Uber’s presence in Arizona’s autonomous vehicle testing scene. |
| [Insert Date – Expansion to other areas] | Expansion of testing to other areas within Arizona. | Multiple locations in Arizona | Increased scope of testing and data collection. |
| [Insert Date – Specific Incident(s) leading to concerns] | [Describe specific incidents, near misses, or minor accidents reported]. | [Location(s) of incidents] | Growing concerns about safety and regulatory compliance. |
| [Insert Date – Fatal Accident] | Fatal accident involving an Uber self-driving vehicle. | [Location of fatal accident] | Immediate suspension of Uber’s self-driving program in Arizona. Significant public outcry and regulatory review. |
The Suspension Incident

Source: fastly.net
Arizona’s suspension of Uber’s self-driving tests got me thinking – sometimes, you need a break from the fast-paced world of autonomous vehicles. Maybe a little downtime with a luxurious read on my kindle oasis in champagne gold is in order. After all, even robots need a recharge, and so do humans dealing with the fallout from these kinds of regulatory decisions.
Back to the news, though – what’s next for Uber’s self-driving ambitions?
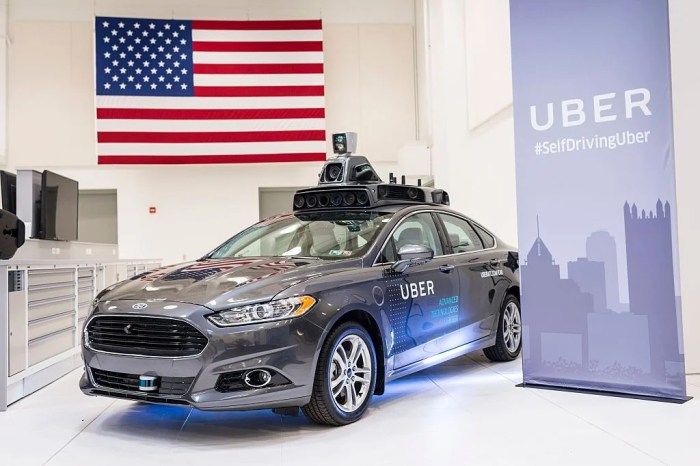
The abrupt halt of Uber’s self-driving car program in Arizona in 2018 wasn’t a gradual fade-out; it was a dramatic crash landing, literally and figuratively. The incident highlighted the complex interplay between technological ambition, regulatory oversight, and public safety concerns surrounding autonomous vehicles. This pivotal moment significantly impacted the trajectory of Uber’s self-driving ambitions and sparked a wider debate about the responsible development and deployment of this transformative technology.
The incident that triggered the suspension involved a fatal accident. This wasn’t just any accident; it involved a pedestrian death, irrevocably shifting the narrative from technological marvel to a stark reminder of the potential risks associated with still-developing autonomous systems. The accident directly involved an Uber self-driving vehicle and a pedestrian crossing the street at night. The collision, and the subsequent investigation, brought intense scrutiny to Uber’s safety protocols and the regulatory framework governing autonomous vehicle testing.
The Accident Details
The accident occurred on March 18, 2018, in Tempe, Arizona. A Volvo XC90 SUV, operating in autonomous mode under Uber’s self-driving program, struck and killed Elaine Herzberg, a 49-year-old pedestrian who was pushing a bicycle across the road outside of a designated crosswalk. The vehicle was traveling at approximately 40 mph. The safety driver, Rafaela Vasquez, was behind the wheel, but was reportedly distracted and failed to intervene before the collision. The accident happened at night, under conditions that likely posed additional challenges for the autonomous system’s perception capabilities. The investigation revealed that the vehicle’s software detected Herzberg approximately six seconds before impact, but the braking system was not activated in time.
Key Players and Reactions, Arizona suspends uber self driving tests
The incident involved several key players. Uber, naturally, was at the center of the controversy, facing immediate public backlash and intense scrutiny from regulatory bodies. Arizona Governor Doug Ducey swiftly suspended Uber’s autonomous vehicle testing permits in the state following the accident. Federal agencies, including the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB), launched their own investigations into the incident. The Tempe Police Department also played a critical role in the initial investigation and accident reconstruction.
The immediate reactions were swift and varied. Uber suspended its autonomous vehicle testing programs across the country. Public outcry focused on questions of safety, accountability, and the ethical implications of deploying autonomous vehicles before they were fully ready. Arizona officials expressed concerns about the safety of Uber’s technology and the adequacy of its safety protocols. The incident prompted a national conversation about the need for stricter regulations and oversight of autonomous vehicle development and testing. The family of Elaine Herzberg filed a wrongful death lawsuit against Uber. The incident remains a pivotal case study in the ongoing development and deployment of self-driving technology.
Arizona’s Regulatory Response
The Arizona Governor’s swift suspension of Uber’s self-driving car testing program sent shockwaves through the burgeoning autonomous vehicle industry. The move highlighted the complex regulatory landscape surrounding this rapidly evolving technology and underscored the potential for significant legal ramifications when safety concerns arise. Arizona’s response wasn’t simply a knee-jerk reaction; it was a carefully considered (or so it seemed) action based on a perceived violation of existing regulations and a broader concern for public safety.
The Arizona Department of Transportation (ADOT), the state’s regulatory body for autonomous vehicles, issued a statement announcing the suspension following the fatal accident involving an Uber self-driving car. The statement emphasized the ADOT’s commitment to public safety and its expectation that all autonomous vehicle testing programs operate within the established legal framework. While the statement didn’t explicitly detail all the alleged violations, it made it clear that Uber’s actions were deemed unacceptable and that the suspension would remain in effect pending a thorough investigation. The statement’s tone was firm, signaling a willingness to enforce regulations, even against major tech companies.
Regulations Allegedly Violated by Uber
Uber’s alleged violations centered around the operation of its self-driving vehicles in a manner inconsistent with its permit and Arizona’s regulatory framework. While the precise details were revealed piecemeal during the subsequent investigations, the core issue revolved around the level of human oversight during testing. Arizona’s regulations likely required a certain level of human intervention and control, especially in situations deemed high-risk. The investigation uncovered that the safety driver in the fatal accident was not adequately attentive, potentially indicating a failure to comply with the mandated level of human oversight. This was further complicated by reports suggesting the safety driver was streaming a video shortly before the collision. This lack of attention, coupled with the severity of the accident, formed the basis for the suspension and subsequent legal actions.
Arizona’s Legal Framework for Autonomous Vehicle Testing
Arizona’s legal framework for autonomous vehicle testing, while relatively progressive, is not without its limitations. The state has a permitting process for companies wishing to test self-driving cars on public roads. These permits stipulate specific requirements, including insurance coverage, safety protocols, and reporting procedures. The specifics of these requirements are often kept confidential for competitive reasons, making a detailed comparison with other states difficult. However, the underlying principle is a commitment to public safety, balanced against the need to foster innovation in the autonomous vehicle sector. The legal framework relies heavily on a system of permits and ongoing monitoring, with provisions for suspension or revocation of permits in the event of serious violations or safety incidents. The framework also likely includes provisions for data collection and reporting to track the performance and safety of autonomous vehicles.
Comparison with Other States’ Regulatory Approaches
Arizona’s approach to regulating autonomous vehicle testing can be compared to other states with similar programs. While the specific regulations vary, the overarching goal of public safety remains consistent. However, there are key differences in implementation and enforcement:
- California: California has a more stringent and detailed regulatory framework, requiring more extensive testing and reporting before allowing autonomous vehicles on public roads. Its approach is arguably more cautious than Arizona’s.
- Texas: Texas has a more permissive regulatory environment, with fewer requirements for testing and reporting. This approach prioritizes encouraging innovation over stringent safety regulations.
- Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania’s regulatory approach falls somewhere in between California and Texas, with a moderate level of requirements for autonomous vehicle testing.
These variations reflect differing priorities and risk tolerances among states. Arizona’s regulatory response to the Uber incident highlights the inherent challenges in balancing innovation with safety concerns in the rapidly evolving field of autonomous vehicles.
Impact of the Suspension on Uber and the Autonomous Vehicle Industry
The Arizona suspension of Uber’s self-driving car tests sent shockwaves through both Uber itself and the wider autonomous vehicle industry. The incident highlighted the significant risks – financial, reputational, and developmental – associated with deploying this cutting-edge technology prematurely. The immediate fallout was substantial, but the long-term implications remain to be seen.
The suspension’s impact reverberated across multiple facets of the industry, prompting a reassessment of safety protocols, regulatory frameworks, and public perception. The financial ramifications for Uber, the reputational damage to its brand, and the broader implications for the autonomous vehicle sector are all intertwined and crucial to understanding the long-term consequences of this pivotal event.
Financial Impact on Uber’s Self-Driving Program
The suspension directly impacted Uber’s self-driving program’s financial performance. Costs associated with the program, including research and development, infrastructure, and personnel, continued to accrue despite the halt in testing. Lost opportunity costs, resulting from the delay in data collection and potential revenue generation through autonomous ride-sharing services, further exacerbated the financial burden. The legal fees associated with the incident and subsequent investigations also contributed significantly to the overall financial strain. Estimates of the direct financial losses are difficult to quantify precisely, but the disruption certainly set back the program’s projected timeline and profitability. This scenario is analogous to the setbacks experienced by other tech companies facing regulatory hurdles or product recalls, where significant financial resources are diverted from core operations to address the crisis.
Reputational Damage to Uber’s Brand
The accident and subsequent suspension severely damaged Uber’s reputation. The incident fueled existing concerns about the company’s safety practices and corporate culture. Negative media coverage amplified public anxieties about the safety of self-driving technology, casting a shadow over Uber’s brand image and potentially impacting consumer trust in its other services. The negative publicity likely resulted in a decline in ridership, investor confidence, and recruitment of top talent, all impacting the company’s long-term viability and ability to attract investment for its autonomous vehicle division. This reputational damage is comparable to the fallout experienced by companies following major product safety failures or ethical scandals, where regaining consumer trust requires extensive efforts and significant investment in rebuilding a positive image.
Broader Impact on the Development and Deployment of Autonomous Vehicles
The Arizona suspension had a chilling effect on the broader autonomous vehicle industry. The incident highlighted the potential for unforeseen safety risks and regulatory uncertainties associated with the deployment of self-driving technology. Investors became more cautious, and several companies reassessed their timelines and strategies for deploying autonomous vehicles. Regulatory bodies worldwide increased scrutiny of autonomous vehicle testing and deployment protocols, leading to stricter regulations and more rigorous safety standards. This cautionary tale served as a reminder of the need for robust safety protocols, transparent testing procedures, and collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders and regulators to ensure the safe and responsible development of this transformative technology. The long-term effect could be a slower, more cautious, but ultimately safer approach to the development and deployment of self-driving vehicles.
Hypothetical Scenario: Long-Term Consequences of the Suspension
Imagine a scenario where the Arizona suspension leads to a significant increase in regulatory hurdles and insurance costs for autonomous vehicle development. This could stifle innovation, limit the number of companies actively pursuing self-driving technology, and potentially delay the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles by several years. In this scenario, smaller companies with less financial resilience might be forced to abandon their projects, while larger companies like Uber might focus more on incremental improvements to existing technologies rather than pursuing fully autonomous systems. This could lead to a more fragmented and less competitive autonomous vehicle market, potentially limiting the societal benefits of this transformative technology. This outcome mirrors the development of other technologies where regulatory uncertainty and high barriers to entry have slowed innovation and limited market penetration.
Post-Suspension Actions and Future Implications

Source: s-nbcnews.com
The Uber self-driving program’s suspension in Arizona sent shockwaves through the autonomous vehicle industry. The immediate aftermath saw a flurry of activity, from damage control to program overhauls, leaving a lasting impact on the future of self-driving technology testing and regulation. Understanding Uber’s response and the subsequent changes is crucial to assessing the long-term viability of autonomous vehicle development.
Uber’s response to the suspension was swift, if somewhat reactive. They immediately halted testing in Arizona and publicly apologized for the incident. Internally, a comprehensive review of their safety protocols and testing procedures was launched. This involved not only examining the specific circumstances that led to the accident but also a broader assessment of their operational framework. The company emphasized its commitment to safety and highlighted its intention to regain public trust. Beyond apologies and internal reviews, Uber also pledged increased investment in safety technology and driver training. The accident served as a stark reminder of the potential risks involved in deploying autonomous vehicles on public roads.
Uber’s Program Modifications
Following the thorough internal review, Uber implemented several significant changes to its self-driving program. These modifications focused primarily on enhancing safety protocols and improving the overall performance of their autonomous driving system. For instance, they increased the level of human oversight during testing, deploying more safety drivers to monitor the system’s behavior and intervene if necessary. Additionally, Uber invested in more sophisticated sensor technologies and software updates designed to improve the system’s ability to perceive and react to its environment, particularly pedestrians and cyclists. They also implemented more rigorous testing procedures, incorporating more diverse and challenging driving scenarios into their simulation and real-world testing programs. These changes aimed to reduce the likelihood of future incidents and demonstrate a commitment to responsible innovation.
Future of Self-Driving Tests in Arizona
The future of self-driving tests in Arizona remains uncertain. While the state has a history of being relatively permissive towards autonomous vehicle testing, the Uber incident undoubtedly heightened regulatory scrutiny. The state is likely to implement stricter guidelines and oversight mechanisms for future testing permits. This might involve more rigorous safety assessments, increased reporting requirements, and potentially more stringent limitations on testing environments and conditions. Whether Uber will resume testing in Arizona depends on their ability to satisfy these new requirements and rebuild trust with state regulators. Other companies involved in autonomous vehicle testing in Arizona may also face heightened scrutiny and stricter regulations. The incident set a precedent, influencing how other states approach the regulation of autonomous vehicle testing.
Recommendations for Improving Safety and Regulatory Oversight
Improving safety and regulatory oversight in autonomous vehicle testing requires a multi-faceted approach. A robust regulatory framework is crucial, one that balances innovation with public safety. This necessitates:
- Standardized Testing Procedures: The development of nationally recognized, standardized testing procedures to ensure consistent and rigorous evaluation of autonomous vehicle systems across different jurisdictions.
- Increased Transparency: Requiring greater transparency from autonomous vehicle companies regarding their testing data, safety protocols, and incident reports. This allows for independent analysis and verification of claims regarding safety and performance.
- Enhanced Data Sharing: Facilitating the sharing of data between autonomous vehicle companies, regulatory bodies, and researchers to identify common challenges and develop best practices for safety.
- Improved Public Engagement: Engaging the public in the conversation surrounding autonomous vehicle technology to address concerns and build trust. This includes transparent communication about testing programs and their potential risks and benefits.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Implementing ongoing monitoring and evaluation of autonomous vehicle testing programs to identify and address potential safety issues in a timely manner.
Public Perception and Media Coverage: Arizona Suspends Uber Self Driving Tests

Source: cnbc.com
The suspension of Uber’s self-driving car tests in Arizona ignited a firestorm of public debate and intense media scrutiny. Public reaction was a complex mix of fear, skepticism, excitement, and anger, all heavily influenced by pre-existing biases towards autonomous vehicles and Uber itself. The media, in turn, amplified and shaped these diverse opinions, often through varying lenses of technological optimism, safety concerns, and corporate accountability.
The public’s reaction to the suspension was largely shaped by the specific details emerging from the accident. Initial shock and concern gave way to a spectrum of opinions, ranging from calls for stricter regulation and a complete halt to autonomous vehicle testing to a more nuanced understanding of the complexities involved. Many questioned Uber’s safety protocols and corporate ethics, while others defended the potential benefits of self-driving technology. Social media played a significant role, rapidly disseminating news and opinions, often without the benefit of fact-checking or in-depth analysis. The incident became a lightning rod for broader discussions about the ethical implications of AI, the role of technology in society, and the balance between innovation and safety.
Public Opinion Spectrum
To visualize the range of public opinions, imagine a horizontal bar graph. The leftmost point represents strong opposition to autonomous vehicles, fueled by fear of accidents and job displacement. This segment of the population often viewed the suspension as a necessary and overdue measure. The rightmost point represents strong support for self-driving technology, driven by the promise of increased safety, efficiency, and convenience. This group tended to view the suspension as an overreaction or a setback for technological advancement. The center of the bar would represent a more neutral or undecided stance, where individuals held mixed feelings or required more information before forming a concrete opinion. The length of each segment on the bar would represent the approximate size of each group, with the center segment potentially being the largest, reflecting the complexity and nuance of public opinion.
Media Coverage Analysis
Media coverage varied significantly across different outlets. Technology-focused publications often presented a more balanced perspective, highlighting both the risks and potential benefits of autonomous vehicle technology. However, some leaned towards either celebrating the technological progress or emphasizing the safety concerns, depending on their editorial stance. News outlets with a stronger focus on consumer safety tended to emphasize the accident and its potential implications for public safety, often presenting a more critical view of Uber’s actions. Sensationalist headlines and a focus on negative aspects were common, potentially contributing to public fear and distrust. Conversely, some publications downplayed the significance of the incident, emphasizing the overall safety record of autonomous vehicles and the potential long-term benefits of the technology.
Bias and Misrepresentation in Media Reporting
Some media outlets exhibited bias by focusing disproportionately on negative aspects of the story, potentially neglecting the broader context of autonomous vehicle development and the overall safety record of such technologies. Others displayed bias by presenting information in a way that favored either pro- or anti-technology viewpoints. Misrepresentations could involve exaggerating the frequency of accidents involving self-driving cars, selectively highlighting negative incidents while downplaying successful test runs, or failing to adequately explain the complex technological challenges involved in developing safe autonomous systems. The use of emotionally charged language and dramatic imagery further contributed to the shaping of public perception.
Last Point
The suspension of Uber’s self-driving tests in Arizona serves as a stark reminder of the challenges inherent in deploying autonomous vehicles. While the technology holds immense potential, the safety concerns and regulatory hurdles remain significant. The incident underscores the need for robust safety protocols, clear regulatory frameworks, and ongoing public dialogue to ensure responsible innovation in this transformative sector. The future of self-driving cars is still unwritten, but this episode provides a critical case study in the balancing act between technological advancement and public safety.