Boeings 737 max safety analysis was reportedly flawed – Boeing 737 Max safety analysis was reportedly flawed, a revelation that sent shockwaves through the aviation world. This wasn’t just a minor oversight; it exposed deep-seated issues within the design, certification, and pilot training processes surrounding this widely used aircraft. The story unfolds with a focus on the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS), a seemingly innocuous piece of software that became the epicenter of a global crisis, grounding fleets and raising serious questions about safety protocols. We’ll delve into the specifics of the reported flaws, examining how discrepancies between initial assessments and subsequent findings led to tragic consequences.
This deep dive explores the intricate details of the MCAS system, its intended function, and the algorithms driving its behavior. We’ll compare it to similar systems in other Boeing aircraft, highlighting key differences that may have contributed to the 737 Max’s unique vulnerabilities. The investigation also examines the role of pilot training, regulatory oversight, and the devastating impact on public trust and airline operations. Get ready for a gripping account of a critical moment in aviation history.
Regulatory Oversight and Certification Process: Boeings 737 Max Safety Analysis Was Reportedly Flawed
The Boeing 737 MAX crisis highlighted critical flaws in the regulatory oversight and certification process, raising serious questions about the effectiveness of existing mechanisms and prompting calls for significant reform. This section examines the roles of regulatory bodies, analyzes the oversight of the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS), compares international certification processes, and proposes improvements to enhance aircraft safety.
The certification process, a complex interplay between manufacturers and regulatory authorities, aims to ensure aircraft meet stringent safety standards before entering commercial service. In the case of the 737 MAX, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States played a central role, delegating significant aspects of the certification process to Boeing itself. This level of delegation, while intended to streamline the process, ultimately contributed to insufficient independent scrutiny of the MCAS system.
FAA’s Role in 737 MAX Certification
The FAA’s oversight of the 737 MAX certification process was significantly affected by its reliance on Boeing’s self-certification. This approach, while efficient in theory, proved insufficient in practice. The FAA’s failure to thoroughly assess the MCAS system’s design, functionality, and potential risks led to a certification that ultimately proved inadequate. This delegation model, criticized for creating a conflict of interest, allowed Boeing to exert undue influence over the safety assessment process. The subsequent investigations revealed a lack of rigorous independent verification and validation, highlighting the need for a more robust and independent oversight mechanism. The FAA’s subsequent reforms, including increased direct oversight and a reassessment of its delegation practices, are attempts to address these deficiencies.
Effectiveness of MCAS Oversight
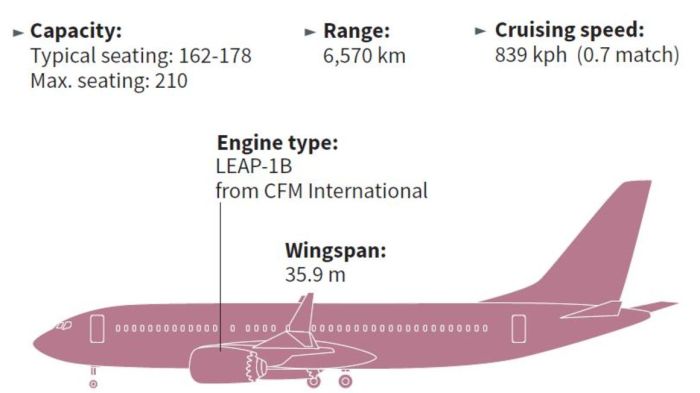
The MCAS system, designed to prevent stalls at high angles of attack, was a central factor in the 737 MAX crashes. The oversight of this system proved ineffective due to several factors, including inadequate documentation of its functionality and limitations, insufficient pilot training regarding its behavior, and a lack of independent validation of its safety. The MCAS’s design, overly reliant on a single angle-of-attack sensor, proved vulnerable to erroneous inputs, leading to unintended and catastrophic consequences. Furthermore, the lack of transparency regarding the MCAS’s capabilities and limitations contributed to the inadequate pilot training that exacerbated the system’s flaws. The investigations highlighted the need for more robust system design, redundancy, and pilot training protocols.
International Certification Process Comparisons, Boeings 737 max safety analysis was reportedly flawed
The 737 MAX certification process differed significantly across various countries. While the FAA’s certification was central, other aviation authorities, such as the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), also played a role. Comparisons revealed differences in the level of scrutiny, the extent of delegation to manufacturers, and the rigor of the independent verification processes. These differences underscore the inconsistencies in international aviation safety standards and highlight the need for greater harmonization and cooperation among global regulatory bodies to ensure a consistent and rigorous certification process worldwide. A more unified approach, with enhanced information sharing and collaborative reviews, could prevent similar situations from recurring.
Proposed Improvements to the Regulatory Framework
Several improvements could enhance the regulatory framework and mitigate future risks. These include: increased independent oversight of aircraft certification, reducing reliance on manufacturer self-certification; stricter requirements for pilot training, emphasizing system limitations and emergency procedures; enhanced transparency in the certification process, providing greater access to information for independent scrutiny; and greater international cooperation and harmonization of safety standards, promoting a consistent global approach to aircraft certification. The implementation of these measures would significantly strengthen the regulatory framework, improving aircraft safety and preventing future crises.
Impact on Public Trust and Airline Operations
The grounding of the Boeing 737 MAX, following two fatal crashes, sent shockwaves through the aviation industry. The event significantly impacted public trust, airline operations, and the overall perception of aviation safety. The ripple effects were far-reaching, affecting not only the airlines directly involved but also the broader travel landscape.
The grounding’s impact on public trust was immediate and profound. News coverage of the crashes, coupled with revelations about potential design flaws and regulatory oversight failures, fueled widespread anxiety and skepticism about air travel safety. Passenger confidence plummeted, leading to a decline in bookings and a general reluctance to fly, particularly on Boeing aircraft. This erosion of trust extended beyond the 737 MAX, impacting the overall reputation of the aviation industry and Boeing itself. Rebuilding this trust required significant effort from Boeing, regulatory bodies, and airlines, involving comprehensive safety reviews, transparent communication, and demonstrable improvements in safety protocols.
Financial Losses and Scheduling Disruptions for Airlines
The 737 MAX grounding resulted in substantial financial losses for airlines that operated the aircraft. These losses stemmed from several factors, including the inability to utilize grounded aircraft, the need for costly modifications and retraining, and the decreased passenger demand resulting from the negative publicity. Airlines faced significant revenue shortfalls, impacting their bottom lines and forcing them to adjust their financial projections. Furthermore, the grounding led to widespread scheduling disruptions. Airlines had to scramble to rearrange flight schedules, often resorting to using alternative aircraft or canceling flights altogether. This resulted in passenger inconvenience, delays, and increased operational costs. For example, Southwest Airlines, a major operator of the 737 MAX, experienced significant revenue losses and had to adjust its flight schedules extensively, leading to a period of operational instability.
Adaptation Strategies Employed by Airlines
Faced with the challenges posed by the 737 MAX grounding, airlines implemented various strategies to mitigate the impact. These included leasing alternative aircraft to maintain flight schedules, re-routing flights to avoid relying on the grounded planes, and offering passengers compensation for disrupted travel plans. Some airlines also invested in enhanced communication strategies to keep passengers informed and address their concerns. These adaptive measures, while costly and complex, demonstrated the resilience of the airline industry and its ability to navigate unforeseen crises. However, the long-term financial and operational consequences of the grounding continued to affect airlines for an extended period.
Timeline of the 737 MAX Crisis and its Impact
Imagine a timeline stretching from October 2018 to December 2020. The initial point marks the Lion Air Flight 610 crash, triggering early concerns. The subsequent Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302 crash in March 2019 leads to a global grounding of the 737 MAX. The months that follow are marked by intense investigations, regulatory scrutiny, and Boeing’s efforts to rectify the design flaws. A gradual return to service begins in late 2019 and continues through 2020, but passenger confidence remains fragile. Throughout this period, airlines grapple with financial losses, operational disruptions, and the long process of rebuilding public trust. The timeline visually depicts the cascading effects of the initial crashes, highlighting the length of the crisis and its profound impact on the aviation industry. The visual would show a clear progression from the crashes to the grounding, investigations, fixes, and the eventual, albeit slow, return to service, illustrating the drawn-out nature of the crisis and its lasting consequences.
The Boeing 737 Max saga serves as a stark reminder of the crucial need for rigorous safety analysis, comprehensive pilot training, and robust regulatory oversight in the aviation industry. The reported flaws in the safety analysis were not isolated incidents but rather symptomatic of a larger system failure. The grounding of the 737 Max, the subsequent investigations, and the resulting changes to safety protocols underscore the high stakes involved in air travel and the importance of continuous improvement in safety procedures. While the planes have returned to the skies, the lessons learned from this crisis remain profoundly significant, shaping the future of aviation safety for years to come. The story is a complex one, filled with technical details and human drama, ultimately highlighting the devastating consequences of overlooking critical safety measures.
 Tech Nest Online Berita Teknologi Terbaru
Tech Nest Online Berita Teknologi Terbaru