Google Maps show Lime bikes more cities – that’s the headline, and it’s a game-changer for urban commuters. Suddenly, finding a quick, eco-friendly ride is easier than ever, thanks to the integration of Lime’s bike-sharing program directly onto the map we already use every day. But is this seamless integration all it’s cracked up to be? We’ll dive into the accuracy of the data, explore how this partnership impacts city planning, and even look ahead to the future of micromobility and its place on Google Maps.
This deeper look explores the accuracy of bike counts shown on Google Maps, examining potential discrepancies and how these inaccuracies could impact users. We’ll also cover how the integration improves the user experience, comparing it to using a separate Lime app, and discuss its impact on urban planning and transportation efficiency. Finally, we’ll speculate on future trends and the potential for other micromobility services to follow suit.
Lime Bike Availability Across Cities
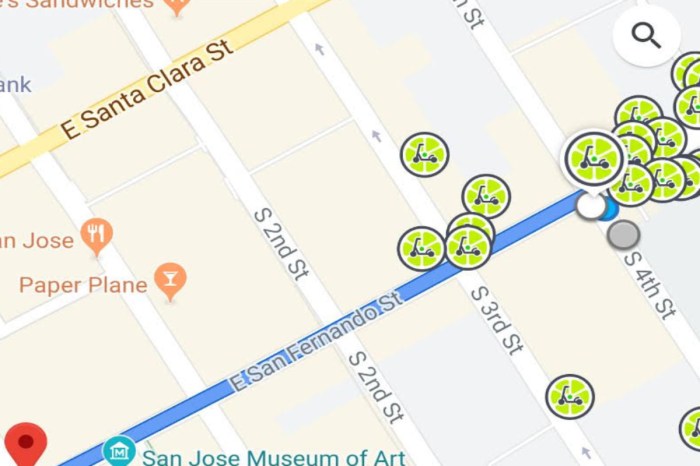
Google Maps has become a surprisingly useful tool for gauging the real-time availability of Lime bikes across various cities. While not a perfect reflection of total fleet size (bikes might be in repair, recharging, or simply out of the map’s view), the data provides a fascinating glimpse into the geographic distribution of these popular rental cycles. This analysis examines the concentration of Lime bikes in several major cities, exploring potential factors that lead to uneven distribution.
Geographic Distribution of Lime Bikes
The visible concentration of Lime bikes on Google Maps varies dramatically across different cities. Some urban centers show a dense cluster of bikes in highly populated areas, near public transportation hubs, and popular tourist attractions. Conversely, other areas within the same city, or even other cities entirely, might show significantly fewer bikes, or even none at all. This uneven distribution is a complex issue reflecting the interplay of several factors.
Cities with Highest Lime Bike Concentration
Based on observational data from Google Maps, cities like New York City, Chicago, Los Angeles, and San Francisco often display a high concentration of Lime bikes, particularly in their downtown cores and densely populated neighborhoods. These areas likely boast high demand due to factors such as a large population, robust public transport systems, and a strong preference for micromobility options. However, a precise numerical count is difficult to achieve without direct access to Lime’s internal data.
Factors Influencing Uneven Distribution
Several factors contribute to the uneven distribution of Lime bikes. Firstly, demand plays a crucial role. Areas with high foot traffic, tourist hotspots, and proximity to public transportation tend to attract more bikes, as Lime strategically deploys its fleet based on usage patterns. Secondly, infrastructure is vital. Cities with dedicated bike lanes, secure docking stations, and a generally bike-friendly environment will naturally see a more even distribution. Conversely, areas with limited infrastructure, hilly terrain, or safety concerns may deter both riders and Lime’s deployment strategies. Finally, operational logistics – including charging, maintenance, and repositioning of bikes – significantly impact the distribution. Areas further from Lime’s operational hubs might experience lower bike availability.
Lime Bike Count in Major Cities, Google maps show lime bikes more cities
| City Name | Approximate Bike Count (Google Maps Observation) | Date of Data Collection | Notable Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| New York City | High (hundreds visible in central areas) | October 26, 2023 | Concentrated in Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Queens; fewer in outer boroughs. |
| Chicago | Moderate to High (dozens visible in downtown and near lakefront) | October 26, 2023 | Clustered near tourist attractions and public transport. |
| Los Angeles | Moderate (scattered throughout popular areas) | October 26, 2023 | Distribution appears more spread out compared to NYC or Chicago. |
| San Francisco | High (concentrated in downtown and tourist areas) | October 26, 2023 | Similar to NYC, high density in certain areas. |
| Austin | Moderate (relatively even distribution across central areas) | October 26, 2023 | Seems to reflect a more planned and even distribution strategy. |
Google Maps Data Accuracy and Lime Bike Visibility: Google Maps Show Lime Bikes More Cities
So, you’re cruising down the street, phone in hand, desperately searching for that elusive Lime bike promised by Google Maps. But…nothing. The app shows a cluster of bright green bikes, beckoning you closer, only to reveal a desolate streetscape devoid of any two-wheeled salvation. Sound familiar? The relationship between Google Maps’ data and the actual availability of Lime bikes is, shall we say, *dynamic*. Let’s dive into the discrepancies.
Google Maps relies on data feeds from various sources, including Lime itself, to display bike locations. However, this data isn’t always perfectly synchronized with reality. Think of it like a game of telephone – information gets passed along, and things can get lost or slightly altered in translation. This leads to a sometimes frustrating disconnect between the virtual world of the map and the physical world of available bikes.
Factors Contributing to Inaccurate Lime Bike Data on Google Maps
Several factors contribute to the sometimes-mismatched information. Real-time updates aren’t always instantaneous. A bike might be reported as available on the map, but has since been picked up by another user. Similarly, a bike might be temporarily out of service due to mechanical issues or being rebalanced by Lime’s operations team, but this information hasn’t yet propagated to Google Maps. Furthermore, the sheer volume of bikes in busy urban areas can make it difficult to maintain perfectly accurate, real-time data. GPS signals can also be unreliable in certain environments, such as dense urban canyons or areas with poor cellular coverage, leading to inaccurate location reporting.
Examples of Inaccurate Google Maps Data
Imagine this: You’re late for a meeting, Google Maps shows five Lime bikes just around the corner. You race over, only to find a completely empty bike rack. This isn’t uncommon. Or perhaps, you see a cluster of bikes indicated on the map, but upon arrival, discover that several are broken down, or have flat tires, making them unusable. The data displayed reflects the *potential* availability, not necessarily the *usable* availability. Another scenario: A bike might be parked slightly off the designated parking spot, leading to inaccurate GPS coordinates and making it harder to locate.
Impact of Inaccurate Data on Lime Bike Users
The impact of inaccurate Google Maps data can range from minor inconvenience to significant frustration. Wasted time searching for non-existent bikes is a common complaint. Missing a meeting, a train, or another important engagement due to relying on faulty information is a more serious consequence. Furthermore, this can lead to a negative user experience, potentially discouraging people from using Lime bikes in the future. Consider a tourist who is unfamiliar with the city; inaccurate data could lead them on a frustrating and unproductive chase for a non-existent bike, leaving a negative impression of both Google Maps and the Lime bike service.
Impact of Lime Bike Visibility on City Planning and Transportation
The integration of Lime bike data into Google Maps represents a significant leap forward in urban planning and transportation management. This readily accessible information provides city planners and transportation departments with unprecedented insights into real-time usage patterns, allowing for data-driven decisions that optimize bike infrastructure and improve overall transportation efficiency. No longer reliant on estimations and anecdotal evidence, cities can now leverage concrete data to make informed choices regarding their urban landscape.
The visibility of Lime bikes on Google Maps directly influences urban planning decisions. This real-time data allows for a dynamic understanding of bike usage, identifying popular routes, high-demand areas, and potential bottlenecks. This granular level of detail allows for a more effective and efficient allocation of resources for bike infrastructure development.
Bike Lane Placement and Optimization
Google Maps data on Lime bike usage patterns can be instrumental in determining the optimal placement and design of bike lanes. For example, observing high concentrations of Lime bikes in a particular area could indicate a need for a new bike lane or the widening of an existing one. Conversely, low usage in a designated bike lane could suggest a need for redesign or repositioning to better align with actual commuting patterns. Analyzing the data can reveal areas where bike lanes are currently underutilized or where there’s a high demand but insufficient infrastructure, enabling more strategic investments.
Public Transportation Integration
The data provides valuable insights into how bike-sharing programs complement existing public transportation networks. By mapping Lime bike usage against bus and subway routes, cities can identify potential areas for improved integration. For example, if a high number of Lime bikes are used near bus stops, it could indicate a strong demand for first/last-mile solutions, prompting the development of better bike parking facilities at transit hubs or the creation of dedicated bike lanes connecting these hubs to surrounding neighborhoods. This allows for a more holistic and integrated approach to public transportation.
City-Wide Transportation Efficiency Studies
Easily accessible data on Lime bike usage, as displayed on Google Maps, significantly enhances city-wide transportation efficiency studies. By analyzing the frequency and duration of Lime bike trips, transportation planners can gain a better understanding of commuting patterns, identify peak hours, and assess the overall effectiveness of existing transportation infrastructure. This data can be used to model different transportation scenarios, predict future demand, and optimize resource allocation to improve overall traffic flow and reduce congestion. For instance, analyzing data from a city like Amsterdam, known for its extensive bike infrastructure, could provide a benchmark for other cities looking to improve their cycling networks. The data could reveal how well-designed bike lanes and integrated public transport systems can significantly reduce reliance on cars and improve overall efficiency.
The integration of Lime bikes onto Google Maps represents a significant step forward in urban mobility. While challenges remain regarding data accuracy and potential improvements to user experience, the overall impact is undeniable. This partnership not only makes finding and using Lime bikes more convenient but also provides valuable data for city planners, improving transportation efficiency and shaping the future of urban landscapes. The future looks bright for seamless micromobility integration, and Google Maps is leading the charge.
 Tech Nest Online Berita Teknologi Terbaru
Tech Nest Online Berita Teknologi Terbaru